Logical Operators
To execute logical operations, logical operators are employed. Boolean expressions are used with logical operators, which return a Boolean value. In loops and decision-making statements, logical operators are combined with conditional operators.
Syntax
operands_one || operands_two;
operands_one && operands_two;
The use of logical operators
#1) Symbol for the Logical AND Operator: "&&" The AND operator returns true when both values are true. It will return false if any of the values are false.
- For example, if both A and B are true, A && B will return true; if either or both are false, it will return false.
#2) Symbol for the Logical OR Operator: "||" The OR operator returns true if any of the conditions/operands are true. When both operands are false, it will return false.
- A || B, for example, returns true if either A or B has a true value. If both A and B are false, it will return false.
#3) Symbol for the Logical NOT Operator: "!" The NOT operator reverses any condition's logical conclusion. The result is false if the condition is true; the result is true if the condition is false.
- For example, if "A||B" returns true,!(A||B) returns false, and if "A||B" returns false, it returns true.
Example Program:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
bool result;
// AND operator
result = (a == b) && (a>b);
cout<<"\n"<<(result);
//OR Operator
result = (a == b) || (a>b);
cout<<"\n"<<(result);
//NOT Operator
result = !((a == b) || (a>b));
cout<<"\n"<<(result);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
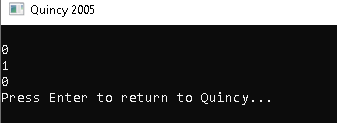
The following is the program's output:
- Because one of the criteria, a==b, is false, the first value will return false.
- As one of the criteria, a > b, is true, the second operator will return true.
- The third operator, which is the negation of the OR result, will yield false.
