Reading and writing in the file
In C ++, files are mainly managed using three streams, streaming, streams found in the fstream headerfile.
ofstream: Stream class to write to files
ifstream: Stream class to read files
fstream: Stream class for reading and writing from/to files.
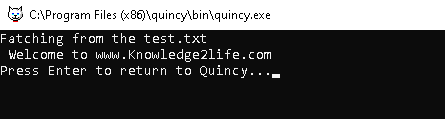
Example Open file using open method:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1;
// Open a file in read mode in your pc
ifstream infile;
infile.open("test.txt");
cout << "Fatching from the test.txt\n";
//Fatching data at the screen
while (infile)
{
getline(infile, str1);
cout << str1;
}
// Close the opened file
infile.close();
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
This requires another standard C ++ library called fstream, which describes three types of data -
ofstream This type of data represents the output of the output and is used to create files and write details to files.
ifstream This type of data represents the input file stream and reads the information in files.
fstream This type of data represents a general file distribution and can both stream and navigate, which means it can create files, record information, and read data to files.
To perform file processing in C ++, the header files and must be included in your C ++ source file.
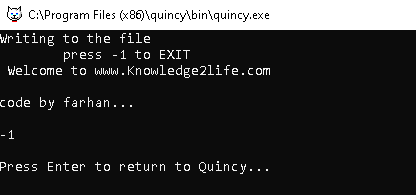
Example write file using outfile method:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1;
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("test.txt");
cout << "Writing to the file" << endl;
cout << "\tpress -1 to EXIT\n";
while (true)
{
getline(cin, str1);
if (str1 == "-1")
break;
outfile << str1;
}
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
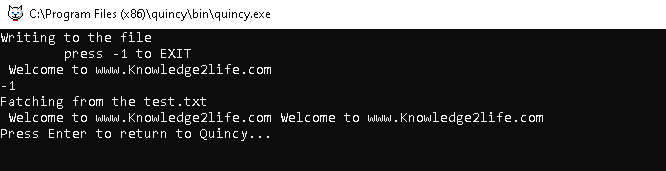
Example:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1;
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("test.txt");
cout << "Writing to the file" << endl;
cout << "\tpress -1 to EXIT\n";
while (true)
{
getline(cin, str1);
if (str1 == "-1")
break;
outfile << str1;
}
outfile.close();
// Open a file in read mode in your pc
ifstream infile;
infile.open("test.txt");
cout << "Fatching from the test.txt\n";
//Fatching data at the screen
while (infile)
{
getline(infile, str1);
cout << str1;
}
// Close the opened file
infile.close();
return 0;
}
OUTPUT: